
Hydrogen sulfide is a gas that gives water a distinctive “rotten egg” odor. While in case of H2S there is no hydrogen bond formation. H2O is liquid because of its ability to form hydrogen bonds which is possible only in case of F, O and N because of their high electronegativity. It is commonly known as hydrosulfuric acid, sewer gas, and stink damp. Hydrogen sulfide is a flammable, colorless gas with a characteristic odor of rotten eggs. What is hydrogen sulfide? Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) occurs naturally in crude petroleum, natural gas, volcanic gases, and hot springs. Here the H2S is donating an electron pair to form a bond to the H of H2SO4, so it is acting as a Lewis base. It is also a Lewis acid, because it is accepting a pair of electrons to form the O-H bond in hydronium ion. H2S is a Brønsted acid, because it is donating a proton to the water. With a boiling point of -60.4 degrees Celsius it is typically found in a gaseous state. H2S is colourless and has a reflective ratio very similar to that of air making it extremely difficult for our eyes to detect. It occurs naturally in crude petroleum, natural gas, and hot springs.

Some common names for the gas include sewer gas, stink damp, swamp gas and manure gas.
#H2S MOLECULAR GEOMETRY FULL#
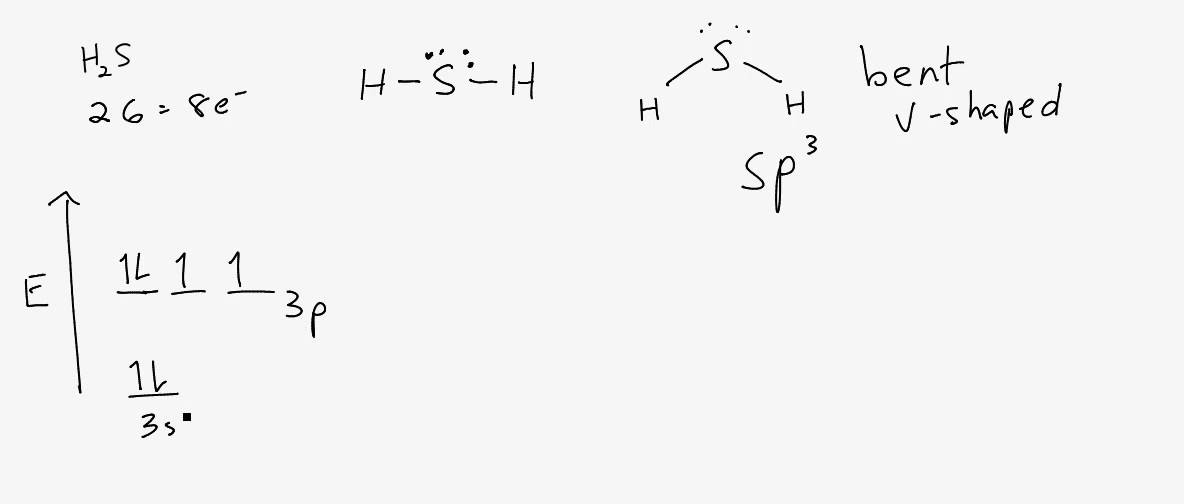
When it dissolves in water, it generates a very weak dibasic acid known as hydro sulfuric acid.Ĭheck the full article “Hydrogen sulfide acid”.Hydrogen sulfide is a colorless, flammable, extremely hazardous gas with a “rot- ten egg” smell. It is soluble in carbon disulfide and mildly soluble in water. H2S (hydrogen sulfide) is a colorless, very deadly gas with a foul stench similar to rotten eggs. In the H2S molecular structure, the sulfur atom is in the center, connecting with two hydrogen atoms, producing a bond angle smaller than 180 degrees. The formula for hydrosulfuric acid, also known as hydrogen sulfide, is H2S. This molecule has two lone pairs and three bound pairs, according to the ClF3 Lewis structure. What is CLF3 molecular geometry?ĬlF3 has a T-shaped molecular geometry and a trigonal bipyramidal electron geometry. it is neutral, but when it is made into an aqueous solution, it releases the hydronium ions H+ and S2- ions. In its gaseous form, H2S is neither acidic nor basic, i.e. The structure is a bent structure with bond angles of 92.1 degrees. Hydrogen sulfide is a polar molecule with a single bond between two hydrogen and sulfur atoms. Explain Hydrogen sulfide Lewis Structure in simple words Some examples of polar molecules are water (H 2O), Ethanol, Ammonia, and SO 2 (Sulfur Dioxide). The slight electrical charges on dissimilar atoms are called partial charges, and the presence of partial charges signifies the occurrence of a polar bond. Specifically, it is found that bonds between atoms of different elements are electrically inequivalent.įor instance, in hydrogen chloride, the H atom is slightly positively charged whereas the Cl atom is slightly negatively charged. The distribution of electrical charge over the atoms joined by the bond causes polarity. Some of the frequently asked questions are given below 1. More Interesting Topics Molar Mass of Acetic Acid| Easy-Explanation Concentration Gradient Definition Sodium Phosphate – Formula, Structure, Types, and Uses Sulfurous Acid| Formula & Lewis Structure Valence Electrons in Nitrogen Is Nh3 Polar? Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Exposure to hydrogen sulfide can be dangerous.
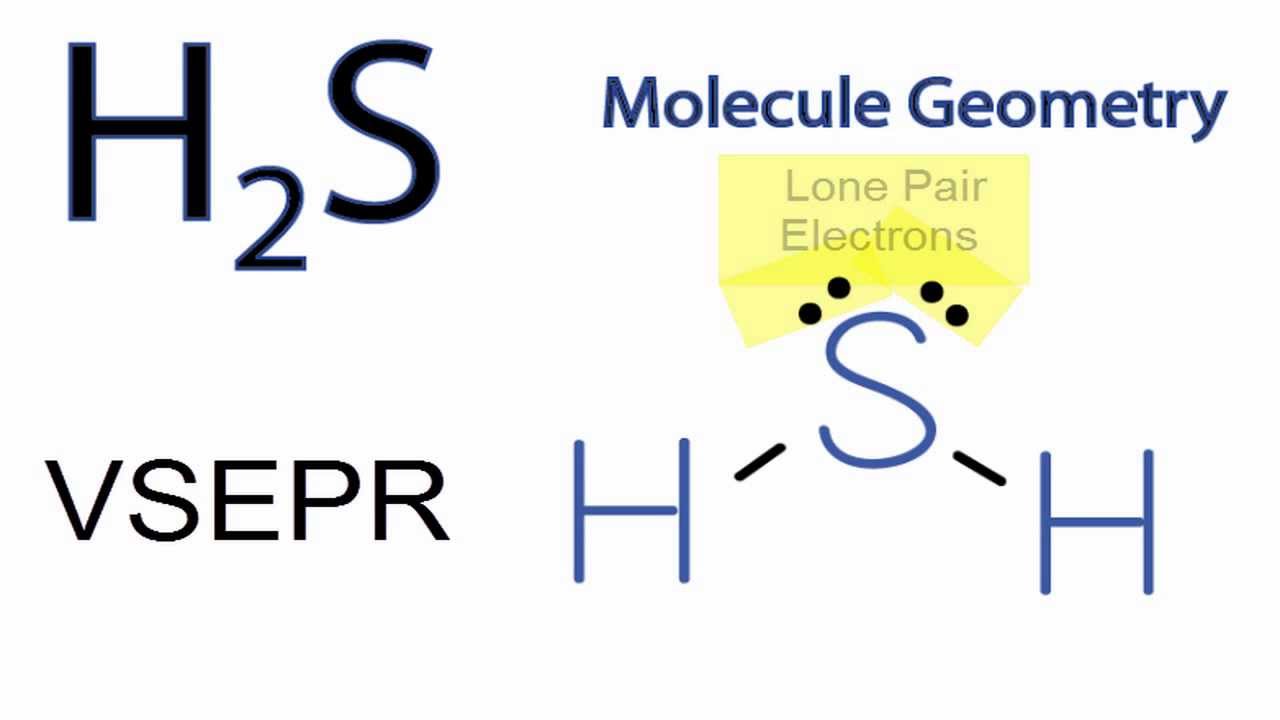
H2S is a polar molecule with a bent geometry.The bond angle is 92.1 degrees, and there are 8 valence electrons.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
